Seismic Considerations For Rack Designs Explored In New RMI Video

Rack safety is critical regardless of a facility’s geographic location. However, depending on the potential for earthquakes in a given region — as well as local building codes — a safe industrial steel storage rack installation may require more stringent design standards. For that reason, the members of the Rack Manufacturers Institute (RMI) have produced and released a new educational video. With just under a four-minute run time, the video explores the various seismic considerations for rack designs.
Regional and Site-Specific Factors

A series of geographic and site-specific factors informs the design, engineering, manufacture, installation, and use of a given rack. To ensure the rack engineer considers all seismic factors prior to designing the rack, the owner must share all relevant information with the rack manufacturer. These include:
- The current edition of the specific building code followed by the state, county, or municipality where the facility is located.
- The address of the rack installation site.
- Any available details about the supporting concrete slab or floor of the building.
- Any information about the soils below the building slab.
Seismic Design Category Identification
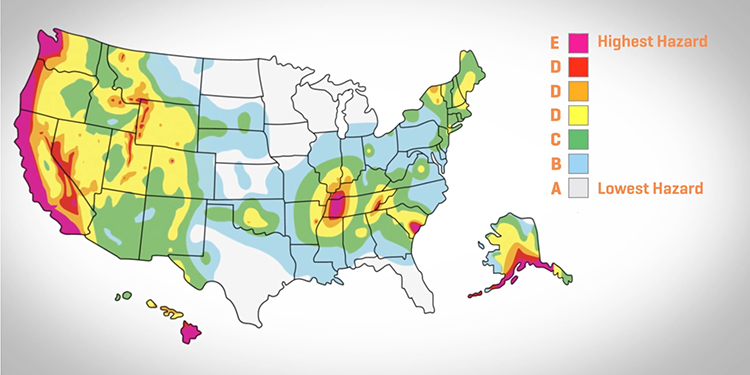
Seismic design categories are classifications assigned to a facility in a given location based on the anticipated severity of ground motion during an earthquake. These categories range from A to F, with A being an area where expected ground shaking is likely to be minor, and F being a major active fault line. Any building classified as a B or higher category will require a seismic force review.
To determine the projected intensity of a potential earthquake in a new rack’s geographic location, consult the Seismic Maps website (www.seismicmaps.org). Here, a building owner can input either the facility’s physical address or coordinates for latitude and longitude. Based on these details, the site shares the location’s seismic parameters. The rack designer and manufacturer will use this information when determining the facility’s seismic design category.
Soil Classification
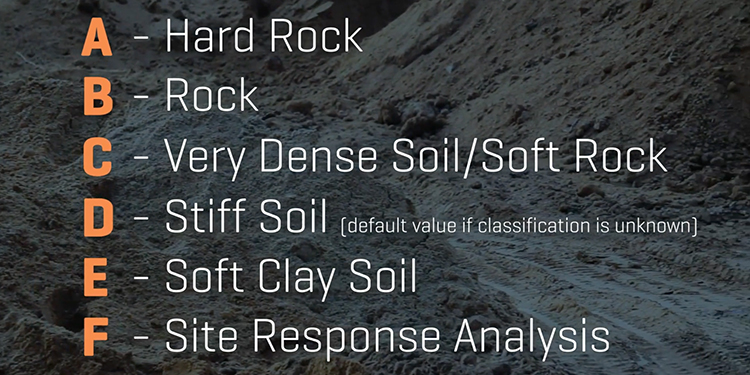
Another key seismic consideration for rack design is the type of soil at the site. There are several soil classifications:
- Class A Soil – Hard rock
- Class B Soil – Rock
- Class C Soil – Very dense soil / soft rock
- Class D Soil – Stiff soil
- Class E Soil – Soft clay soil
A soil engineer determines the class of soil at the facility site. Both the type of soil at the location and the seismic design category of the geographic area are factors in determining the rack’s design. As an example, the video notes that a building in a region with low seismicity but soft soil may still require seismic calculation factors in the rack’s design. Further, if it is not possible to determine the type of soil at a location, the rack’s design must meet Class D Soil requirements for safety.
Impact of Seismic Considerations on Rack Design

Based on the regional and site-specific information about the rack’s location, the engineer will tailor its design for maximum safety. For example, rack installed in areas of high seismicity will require a larger horizontal clearance. Because structures sway side-to-side as the ground moves, the potential for collisions is high. Additional space reduces the risk of the rack impacting another rack or building structures in an earthquake.
Additionally, a seismic event can cause loads to fall off the rack, potentially damaging the building or injuring employees. To prevent this, the rack engineer can specify component enhancements and additional safety features. These include stronger beam-to-column connections, increased bracing, heavier welding, stronger frames and beams, larger base plates, or additional anchors. The video notes that in certain situations the slab may need to be thicker to support the rack and its load.
Seismicity May Preclude Use of Used Rack
Finally, the video reminds viewers that every industrial steel storage rack structure is engineered specifically for a given location and application. Therefore, it may not be possible incorporate used rack components in an installation. That’s because rack originally designed for use in one region may not meet the seismic requirements of a different location.
Watch the Video
Want to Learn More About Safe Rack Installations in Earthquake Zones?
RMI has assembled a list of frequently asked questions and answers specific to seismic considerations for rack design. These cover RMI’s ANSI MHI16.1: Design, Testing, and Utilization of Industrial Storage Racks, rack design reviews, seismic design categories, seismic factors and site coefficients, soil classifications, seismic separation, redundancy, and the newest seismic maps.
Additionally, the Seismic Considerations for Rack Designs video is part of a series. All of RMI’s industrial steel storage rack safety videos are available on its Rack Safety Blog or website.


